Hello, I'm Emily!
(she/her/hers)
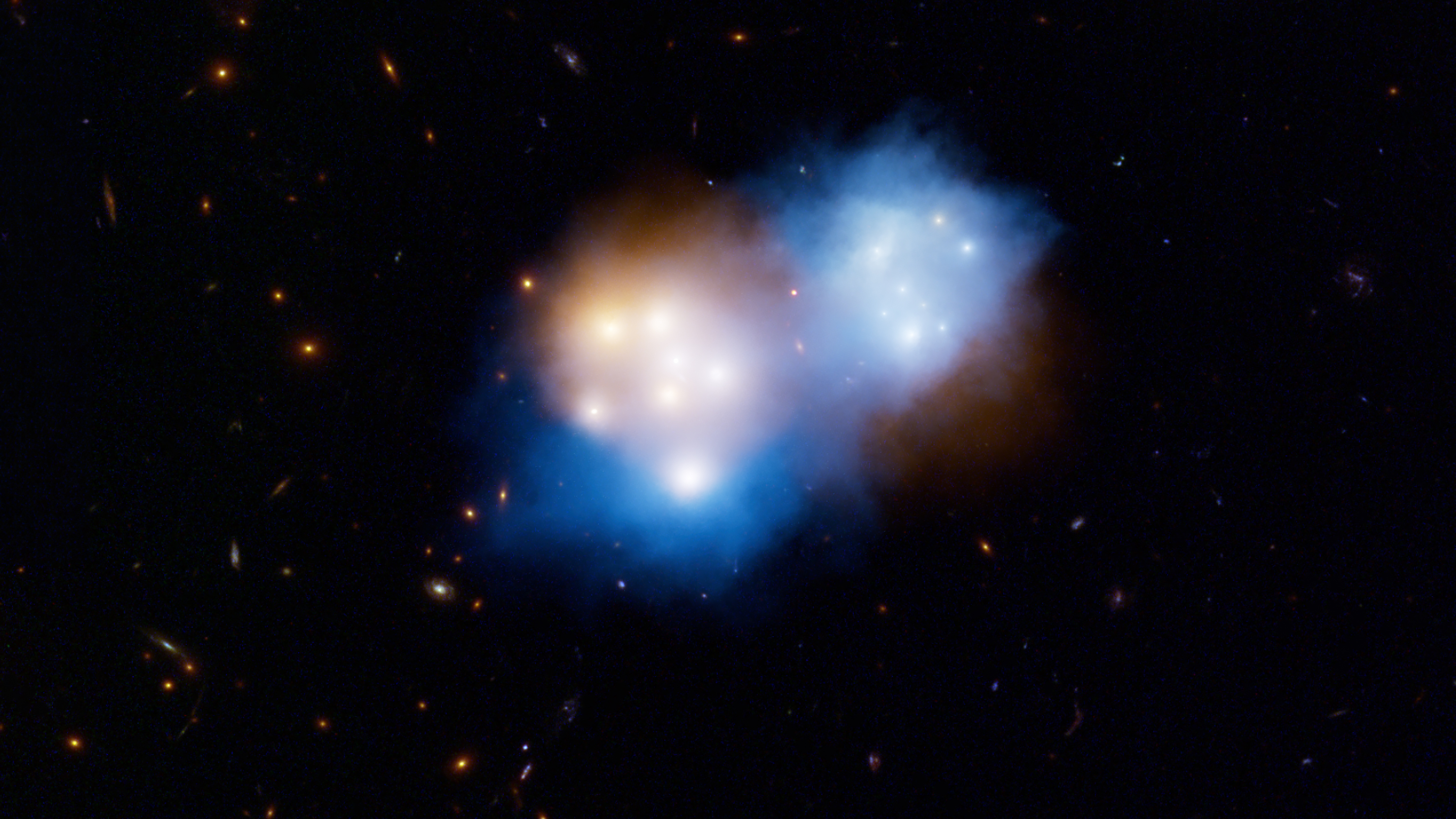
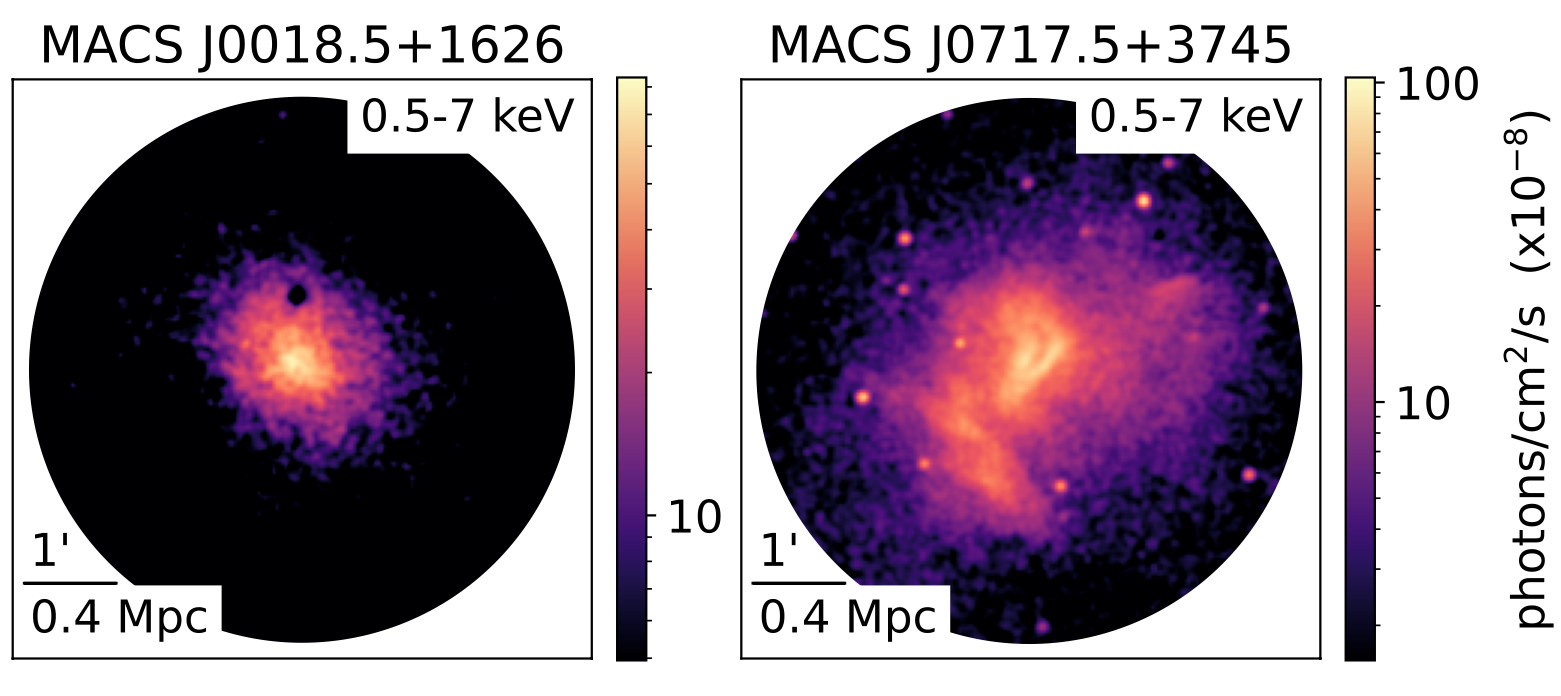
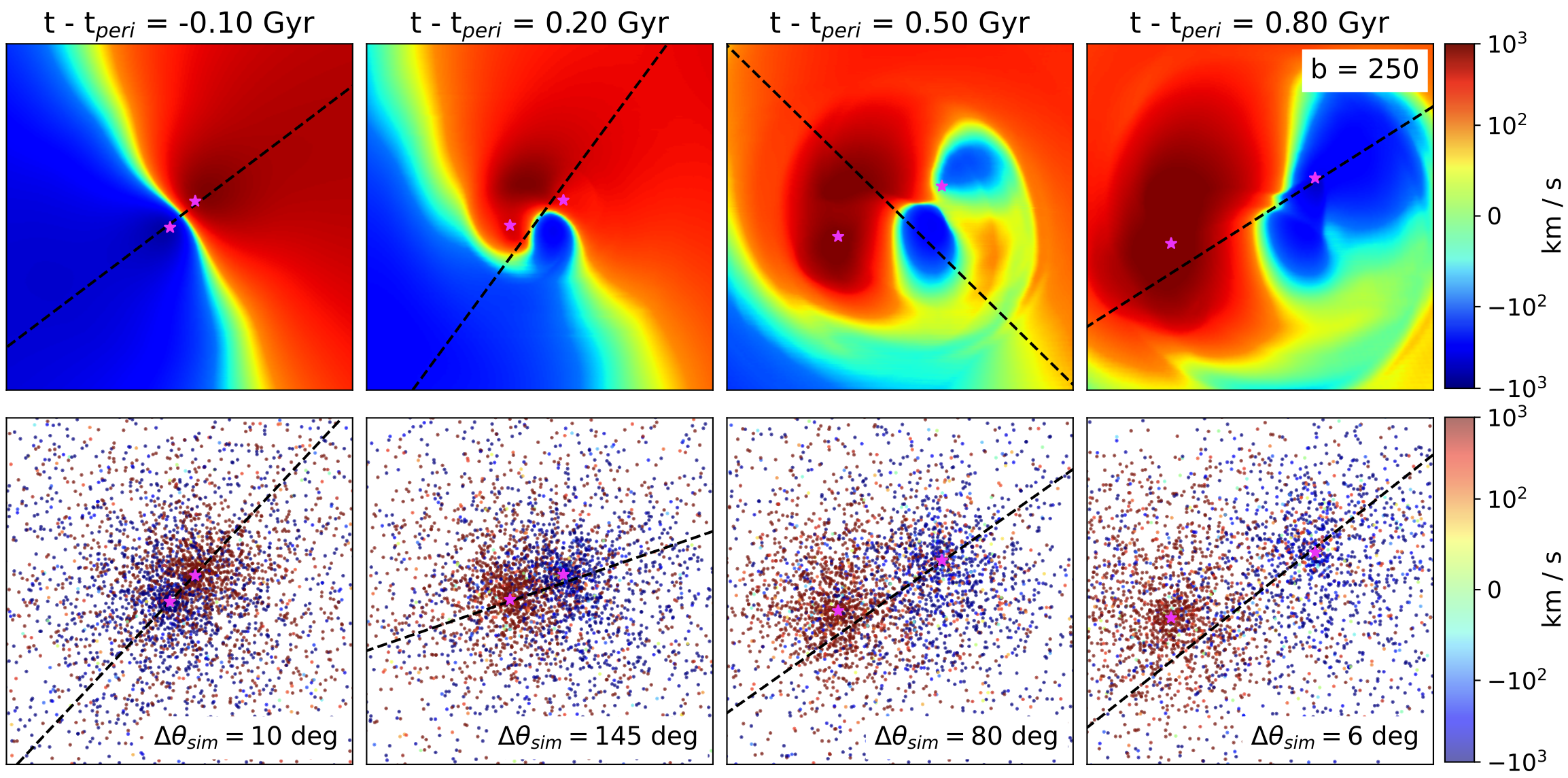
I'm a 5th year PhD candidate and NSF graduate research fellow in astrophysics at Caltech. I work in the Observational Cosmology group to study the dynamics of merging clusters of galaxies using a combination of multiwavelength observations (X-ray, optical, sub-mm) and hydrodynamical simulations of galaxy cluster mergers.
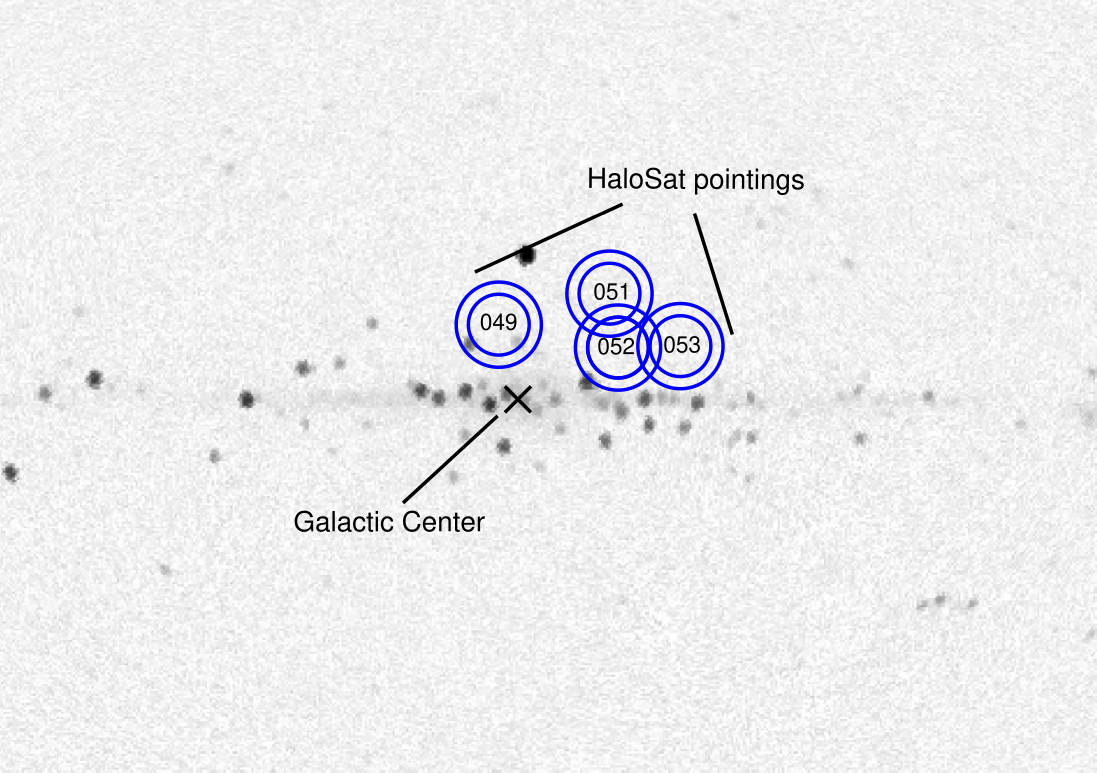
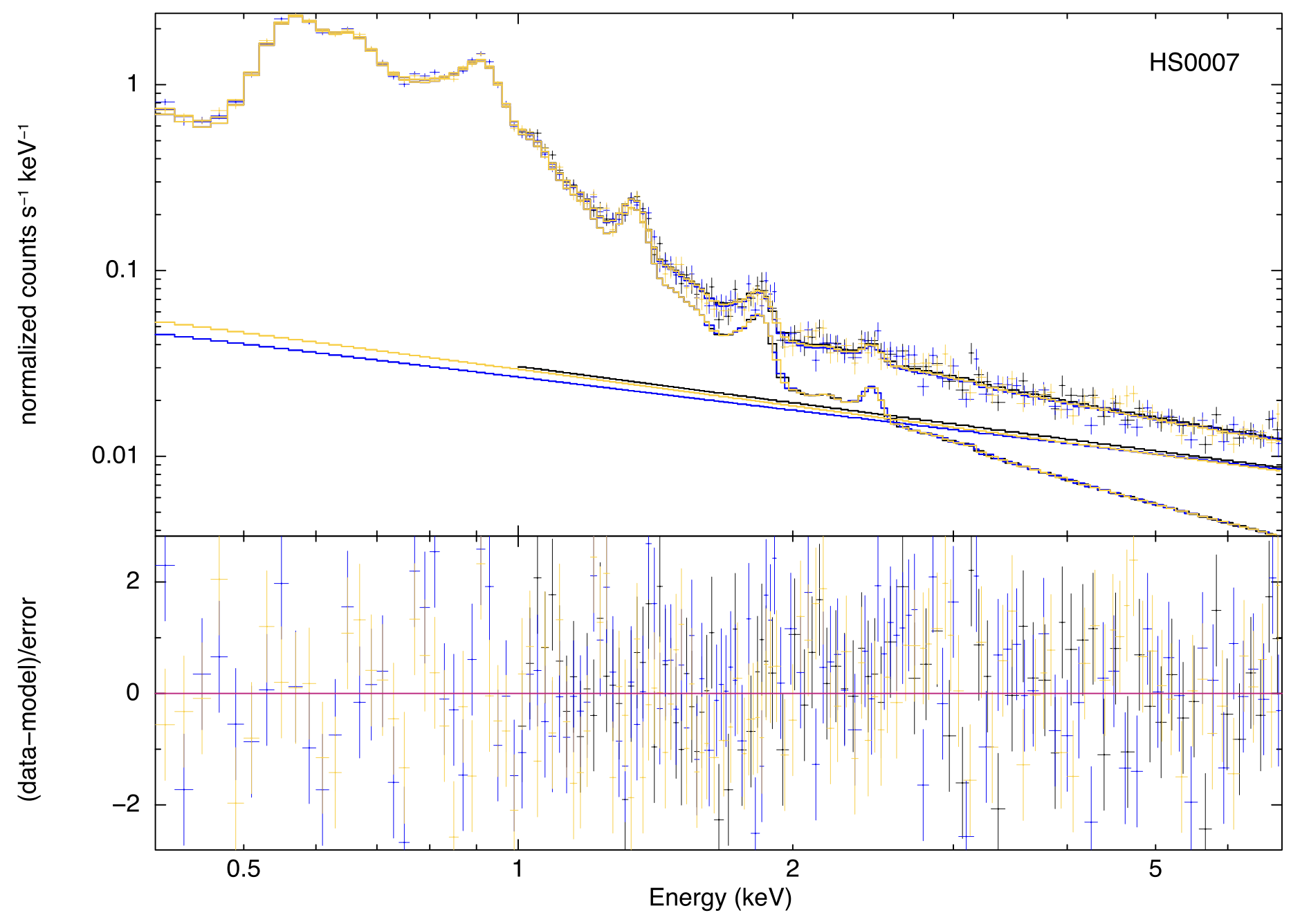
Recently, I finished an SAO predoctoral fellowship at the Center for Astrophysics | Harvard & Smithsonian, where I made predictions for the X-ray signatures of galactic feedback processes in the circumgalactic medium.Before beginning my PhD, I completed my undergrad in astronomy & physics at the University of Iowa and was an intern in the X-ray Astrophysics Laboratory at NASA Goddard Space Flight Center, primarily working on HaloSat.
When not thinking about astronomy, I love to go backpacking, climbing or hiking, to write poetry, and to play the flute.